Painful Peripheral Neuropathy
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
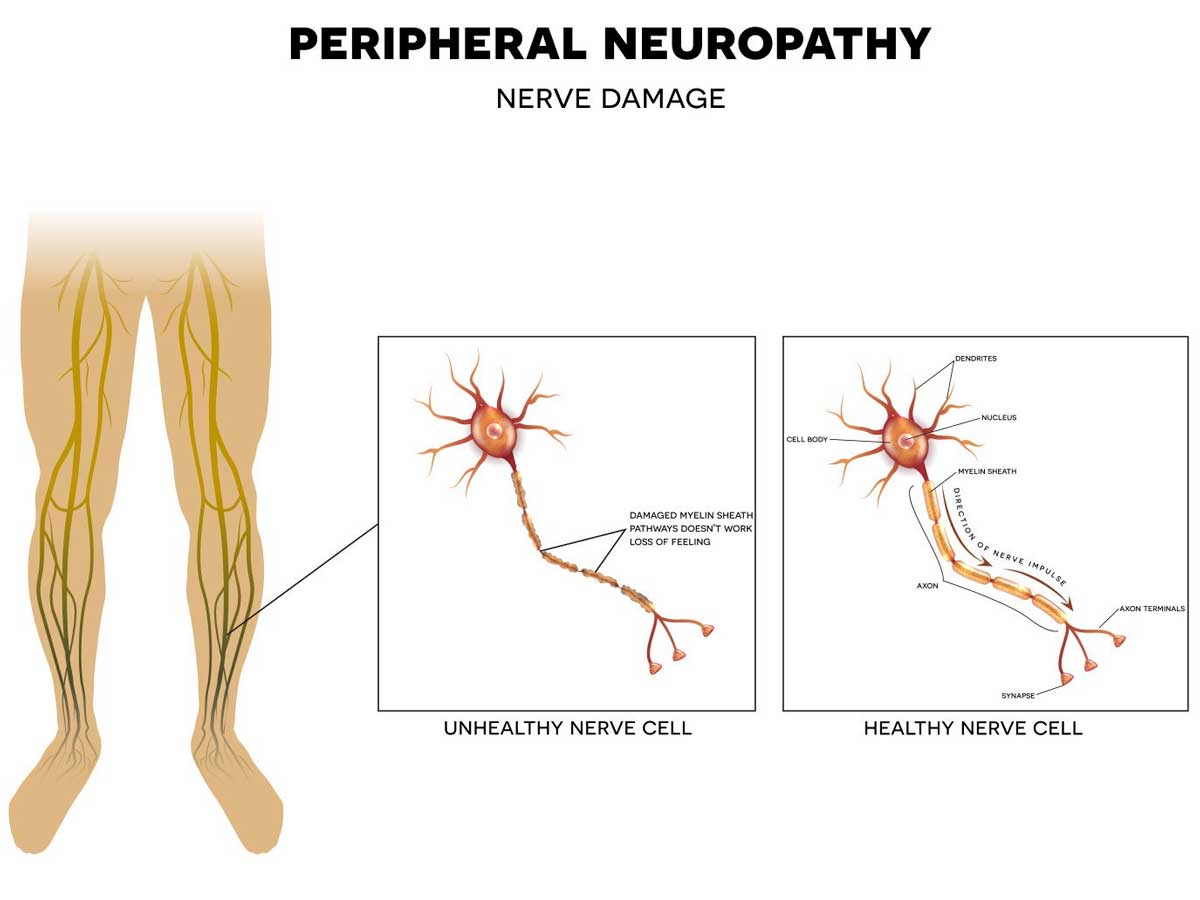
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that affects the peripheral nervous system, which is the network of nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) to the rest of the body. When the peripheral nerves are damaged, it can cause a wide range of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain. These symptoms can be mild or severe and can affect one or multiple areas of the body.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy depend on the type of nerve fibers that are damaged. Sensory nerve fibers carry information about touch, temperature, and pain, and damage to these fibers can cause numbness, tingling, and pain. Motor nerve fibers control muscle movement, and damage to these fibers can cause weakness and muscle wasting. Autonomic nerve fibers control involuntary functions, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and digestion, and damage to these fibers can cause problems with these functions.
Causes:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to diabetic neuropathy.
- Vitamin Deficiencies
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Infections: Certain infections, such as shingles, HIV, and Lyme disease, can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Inherited disorders: Some people inherit genes that make them more susceptible to nerve damage.
- Toxins: Exposure to certain toxins, such as alcohol, heavy metals, and chemotherapy drugs, can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Trauma: Injuries to the nerves, such as from a car accident or sports injury, can cause peripheral neuropathy.
Treatments for Painful Peripheral Neuropathy
Treatment for peripheral neuropathy depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. In some cases, treating the underlying cause can help alleviate symptoms. For example, controlling blood sugar levels in diabetes can help slow the progression of diabetic neuropathy. In other cases, medications such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants can be used to manage symptoms. Physical therapy and occupational therapy may also be helpful in improving muscle strength and function.
Additional treatment options provided at Regenexx Las Vegas.
Nerve Hydrodissection with PRP and Platelet Lysate
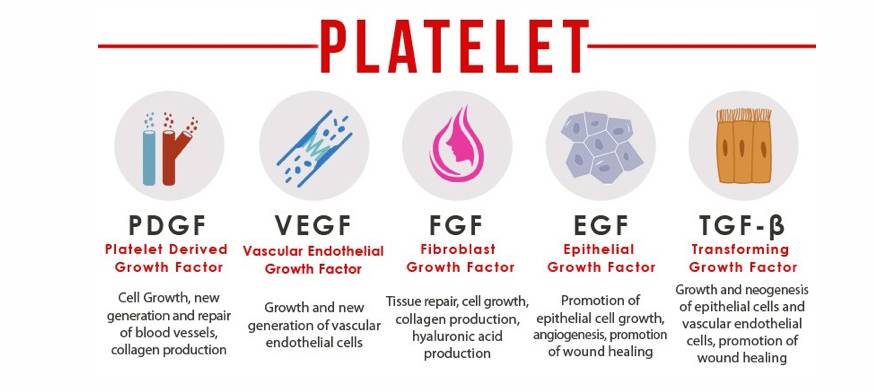
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a treatment that involves the use of the patient’s own blood to promote healing and reduce inflammation in injured tissues. This treatment has been used for a variety of conditions, including peripheral neuropathy.
PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood and processing it to concentrate the platelets, which are rich in growth factors. The concentrated platelets are then injected into the affected area, where they can help to stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
In the case of peripheral neuropathy, PRP therapy may be used to treat nerve damage in the hands or feet. The concentrated platelets can help to promote nerve regeneration and reduce inflammation in the nerves, which can help to alleviate symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling.
PRP therapy is generally considered safe and has few side effects, as the patient’s own blood is used. However, as with any medical procedure, there is always small risks to be considered related to insertion of needles through the skin.
FAQ for PRP for Peripheral Neuropathy
Hidden Accordion - DO NOT DELETE!
How is the Nerve Hydrodissection Performed?
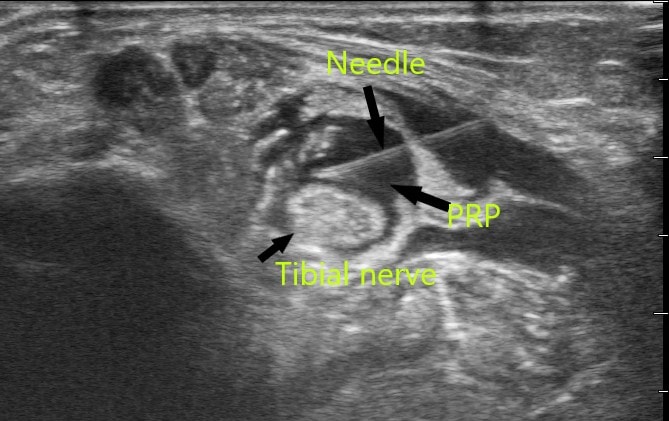 Once we understand which nerves need to be treated, we can utilize ultrasound imaging to identify the nerve. Then, under ultrasound guidance, we can direct a needle attached to a syringe containing the PRP and platelet growth factor solution and inject/hydrodissect any adhesions off the nerve while bathing the nerve with the platelet growth factors.
Once we understand which nerves need to be treated, we can utilize ultrasound imaging to identify the nerve. Then, under ultrasound guidance, we can direct a needle attached to a syringe containing the PRP and platelet growth factor solution and inject/hydrodissect any adhesions off the nerve while bathing the nerve with the platelet growth factors.
How Many Treatments Does it Take to See Improvement?
In general, may take anywhere from 1-3 treatments 6-8 weeks apart. We would evaluate you every 6 weeks to assess symptoms and make treatment decisions based on your response.
How Does PRP Help the Nerve?
PRP can initiate healing through the following:
- Promotes sprouting and growth of nerve fibers (axons)
- Promotes myelin production (protective sheath around nerves)
- Improves growth of blood supply to the nerve
- Decreases scar formation within and around the nerves
- Decreases inflammation of the nerve and surrounding tissue
- Improves Schwann (nerve helper) cell survival, multiplication and activation
- Mobilizes and stimulates fibroblasts and stem cells to heal the nerve
REFERENCES
1. Sánchez, Mikel1,2; Garate, Ane2; Delgado, Diego Ph.D.2,Padilla, Sabino M.D., Ph.D.3.Platelet-rich plasma, an adjuvant biological therapy to assist peripheral nerve repair. Neural Regeneration Research 12(3):p 338, March 2017. | DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.202914
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5319232/pdf/NRR-12-47.pdf
2. Wang S, Liu X, Wang Y. Evaluation of Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: A Critical Review of Literature. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 1;10:808248. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.808248. PMID: 35299637; PMCID: PMC8923347.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8923347/pdf/fbioe-10-808248.pdf
MLS Laser
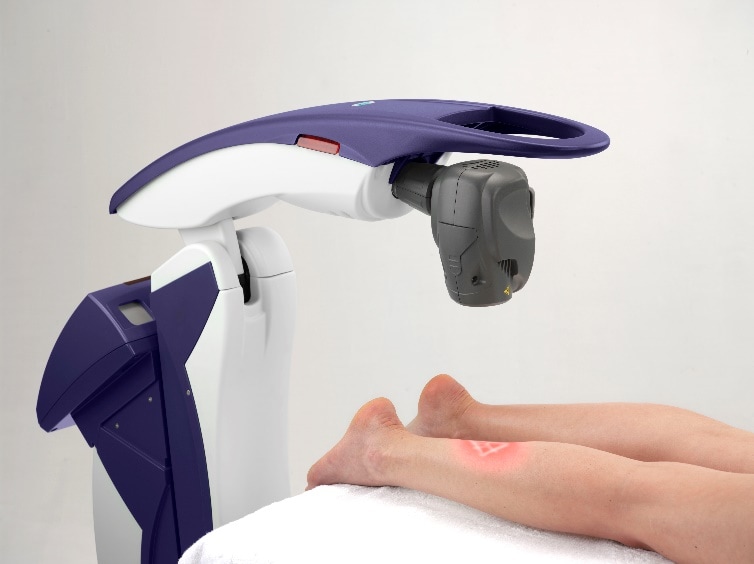
MLS laser therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses specific wavelengths of light to reduce pain, inflammation, and promote tissue healing. This therapy has been used to treat a variety of conditions, including peripheral neuropathy.
In the case of peripheral neuropathy, MLS laser therapy works by targeting the affected nerves with specific wavelengths of light. The light energy penetrates the skin and reaches the underlying nerves, where it can stimulate cellular activity and reduce inflammation, which can help to alleviate symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling.
MLS laser therapy is considered a safe and effective treatment for peripheral neuropathy. The treatment is painless and typically takes less than 30 minutes per session. Most patients experience relief after just a few sessions, although the number of treatments required may vary depending on the severity of the condition.
It is important to note that MLS laser therapy is not a cure for peripheral neuropathy, but rather a complementary therapy that can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as treatment of the underlying cause, medications, and physical therapy.
FAQ for MLS Laser
Hidden Accordion - DO NOT DELETE!
What is Laser Therapy?
Laser therapy uses specific wavelengths of light to treat painful conditions which stimulates intracellular activity, reduces pain/inflammation, and accelerates recovery time.
How Long Does Each Treatment Take?
For peripheral neuropathy involving the lower extremities, the average treatment time is typically 30 minute. We may schedule a longer visit to accommodate changing and positioning of the laser.
How Many Treatments Will I Need?
While one may start to feel some mild improvement over 3 sessions, in general most will need up to 12 sessions to see more extended improvement in their symptoms.
What Does the Treatment Feel Like?
MLS laser therapy is a painless treatment. You may experience a comfortable sensation in area of treatment.
What to Expect After Treatment?
The improvement is typically gradual, and the pain and inflammation can decrease as the laser treatment session plan progresses. Some can respond more quickly than others. Some positive results can be seen between 3-4 treatments, with the average number of treatments being 6-12 treatments. The effects of the MLS laser are cumulative. We recommend completing the entire course of treatment recommended to give the best chance to reduce symptoms
REFERENCES
1. Fallah A, Mirzaei A, Gutknecht N, Demneh AS. Clinical effectiveness of low-level laser treatment on peripheral somatosensory neuropathy. Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Apr;32(3):721-728. doi: 10.1007/s10103-016-2137-y. Epub 2017 Jan 10. PMID: 28074305.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28074305/
2. Cg SK, Maiya AG, Hande HM, Vidyasagar S, Rao K, Rajagopal KV. Efficacy of low level laser therapy on painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Laser Ther. 2015 Oct 2;24(3):195-200. doi: 10.5978/islsm.15-OR-12. PMID: 26557734; PMCID: PMC4639677.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4639677/
3. M A, Ummer V S, Maiya AG, Hande M. Low level laser therapy for the patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy – A systematic review. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019 Jul-Aug;13(4):2667-2670. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.07.035. Epub 2019 Jul 13. PMID: 31405692.